Palliative Care
Palliative Care
Palliative care is a service that focuses on symptom management, comfort, and quality of life for individuals with chronic injury, illness, or disease such as stroke, heart failure, or cancer. Individuals can qualify to receive the care at the time of diagnosis and during curative care efforts. The focus is on providing comfort for the time being rather than prolonging life. An example of palliative care is pain and symptom management related to multiple sclerosis. Palliative care can be provided along with curative treatment. Over time, however, if the doctor and/or the palliative care team believe that the treatment is no longer helping, the doctor may recommend hospice.

Palliative Care Eligibility
The patient must meet all of the general eligibility criteria.
- Is likely to or has started to use the hospital or emergency department as a means to manage the patient’s advanced disease (this refers to unanticipated decompensation and does not include elective procedures.
- Has an advanced illness, as defined in the Section for Disease Specific Eligibility below, with appropriate documentation of continued decline in health status and is not eligible for or declines hospice enrollment.
- Death within a year would not be unexpected based on clinical status.
- Has received appropriate patient-desired medical therapy OR is a patient for whom patient-desired medical therapy is no longer effective. The patient is NOT in reversible acute decompensation.
- The patient and the family/patient-designated support (if applicable) agrees to:
- Attempt, as medically/clinically appropriate, in-home, residential-based, or outpatient disease management/palliative care instead of going to the emergency department first; and
- Participate in Advance Care Planning discussions.
The patient must meet at least one of the four disease-specific eligibility criteria. (If the patient is younger than 21 years old, see Pediatric Palliative Care Eligibility section.)
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- Patient should have both:
- The patient is hospitalized due to CHG as the primary diagnosis with no further invasive interventions planned or meets criteria for the New York Heart Association’s (NYHA) heart failure classification III or higher.
- The patient has an ejection fraction of less than 30% for systolic failure OR significant comorbidities.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Patient should have both:
- The patient has a forced expiratory volume (FEV) of 1 less than 35% of predicted AND a 24-hour oxygen requirement of less than 3 liters per minute.
- The patient has a 24-hour oxygen requirement of greater than or equal to 3 liters per minute.
- Cancer
- Patient should have both:
- The patient has stage III or IV solid organ cancer, lymphoma, or leukemia.
- The patient has a Karnofsky Performance Scale score less than or equal to 70% OR has failure of two lines of standard of care therapy (chemotherapy or radiation therapy).
- Liver Disease
- Patient should have both:
- The patient has stage III or IV solid organ cancer, lymphoma, or leukemia.
- The patient has a Karnofsky Performance Scale score less than or equal to 70% OR has failure of two lines of standard of care therapy (chemotherapy or radiation therapy).
- Or at least 1 of the following:
- The patient has evidence of irreversible liver damage and has a Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score of greater than 19.
- The patient has evidence of irreversible liver damage, serum albumin less than 3.0, an International Normalized Ratio (INR) greater than 1.3.
- Patient should have both:
- Patient should have both:
- Patient should have both:
- Patient should have both:
- Stroke/CVA
- The patient is unable to take oral nutrition, change in mental status, history of aspiration or aspiration pneumonia.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) or End-stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
- Severe Dementia or Alzheimer’s Disease
The patient must meet all of the general eligibility criteria.
General Eligibility Guidelines
Patient should have both:
- The patient is under the age of 21
- The family and/or legal guardian agrees to the provision of pediatric palliative care services.
Disease Specific Eligibility Guidelines
The patient must meet at least one of the four disease-specific eligibility criteria.
- Conditions for which curative treatment is possible, but may fail (e.g. advanced or progressive cancer or complex and severe congenital or acquired heart disease)
- Conditions requiring intensive long-term treatment aimed at maintaining quality of life (e.g. human immunodeficiency virus infection, cystic fibrosis, or muscular dystrophy)
- Progressive conditions for which treatment is exclusively palliative after diagnosis (e.g. progressive metabolic disorders or severe forms of osteogenesis imperfecta)
- Conditions involving severe, non-progressive disability, or causing extreme vulnerability to health complications (e.g. extreme prematurity, severe neurologic sequelae of infectious disease or trauma, severe cerebral palsy with recurrent infection or difficult-to-control symptoms)
The patient must meet all of the general eligibility criteria.
- Is likely to or has started to use the hospital or emergency department as a means to manage the patient’s advanced disease (this refers to unanticipated decompensation and does not include elective procedures.
- Has an advanced illness, as defined in the Section for Disease Specific Eligibility below, with appropriate documentation of continued decline in health status and is not eligible for or declines hospice enrollment.
- Death within a year would not be unexpected based on clinical status.
- Has received appropriate patient-desired medical therapy OR is a patient for whom patient-desired medical therapy is no longer effective. The patient is NOT in reversible acute decompensation.
- The patient and the family/patient-designated support (if applicable) agrees to:
- Attempt, as medically/clinically appropriate, in-home, residential-based, or outpatient disease management/palliative care instead of going to the emergency department first; and
- Participate in Advance Care Planning discussions.
The patient must meet at least one of the four disease-specific eligibility criteria. (If the patient is younger than 21 years old, see Pediatric Palliative Care Eligibility section.)
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- Patient should have both:
- The patient is hospitalized due to CHG as the primary diagnosis with no further invasive interventions planned or meets criteria for the New York Heart Association’s (NYHA) heart failure classification III or higher.
- The patient has an ejection fraction of less than 30% for systolic failure OR significant comorbidities.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Patient should have both:
- The patient has a forced expiratory volume (FEV) of 1 less than 35% of predicted AND a 24-hour oxygen requirement of less than 3 liters per minute.
- The patient has a 24-hour oxygen requirement of greater than or equal to 3 liters per minute.
- Cancer
- Patient should have both:
- The patient has stage III or IV solid organ cancer, lymphoma, or leukemia.
- The patient has a Karnofsky Performance Scale score less than or equal to 70% OR has failure of two lines of standard of care therapy (chemotherapy or radiation therapy).
- Liver Disease
- Patient should have both:
- The patient has stage III or IV solid organ cancer, lymphoma, or leukemia.
- The patient has a Karnofsky Performance Scale score less than or equal to 70% OR has failure of two lines of standard of care therapy (chemotherapy or radiation therapy).
- Or at least 1 of the following:
- The patient has evidence of irreversible liver damage and has a Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score of greater than 19.
- The patient has evidence of irreversible liver damage, serum albumin less than 3.0, an International Normalized Ratio (INR) greater than 1.3.
- Patient should have both:
- Patient should have both:
- Patient should have both:
- Patient should have both:
- Stroke/CVA
- The patient is unable to take oral nutrition, change in mental status, history of aspiration or aspiration pneumonia.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) or End-stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
- Severe Dementia or Alzheimer’s Disease
The patient must meet all of the general eligibility criteria.
- General Eligibility Guidelines
- Patient should have both:
- The patient is under the age of 21
- The family and/or legal guardian agrees to the provision of pediatric palliative care services.
- Disease Specific Eligibility Guidelines
- The patient must meet at least one of the four disease-specific eligibility criteria
- Conditions for which curative treatment is possible, but may fail (e.g. advanced or progressive cancer or complex and severe congenital or acquired heart disease)
- Conditions requiring intensive long-term treatment aimed at maintaining quality of life (e.g. human immunodeficiency virus infection, cystic fibrosis, or muscular dystrophy)
- Progressive conditions for which treatment is exclusively palliative after diagnosis (e.g. progressive metabolic disorders or severe forms of osteogenesis imperfecta)
- The patient must meet at least one of the four disease-specific eligibility criteria
- Patient should have both:
Conditions involving severe, non-progressive disability, or causing extreme vulnerability to health complications (e.g. extreme prematurity, severe neurologic sequelae of infectious disease or trauma, severe cerebral palsy with recurrent infection or difficult-to-control symptoms)
- General Eligibility Guidelines
Palliative Performance Scale (PPS)
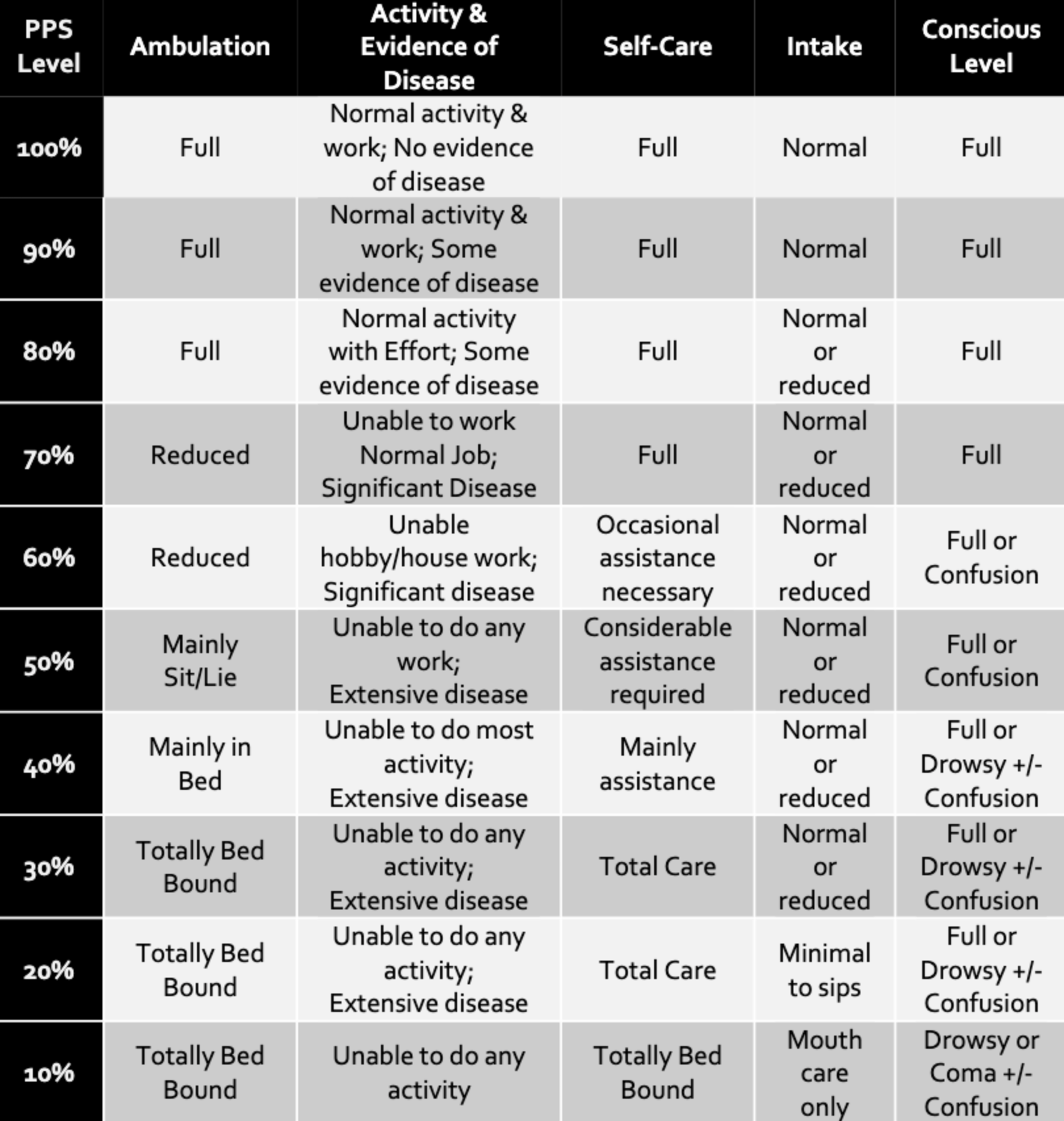
PPS Lavel
Ambulation
Activity & Evidence of Disease
Self Care
Intake
Conscious Level
100%
Full
Normal activity & work; No evidence of disease
Full
Normal
Full
90%
Full
Normal activity & work; Some evidence of disease
Full
Normal
Full
80%
Full
Normal activity with effort; Some evidence of disease
Full
Normal or reduced
Full
70%
Reduced
Unable to work normal job; Significant Disease
Full
Normal or reduced
Full
60%
Reduced
Unable hobby/house work; Significant Disease
Occasional assistance necessary
Normal or reduced
Full or Confusion
50%
Mainly Sit/Lie
Unable to do any work; Extensive Disease
Considerable assistance required
Normal or reduced
Full or Confusion
40%
Mainly in Bed
Unable to do most activity; Extensive Disease
Mainly assistance
Normal or reduced
Full or Drowsy +/- Confusion
30%
Totally Bed Bound
Unable to do any activity; Extensive Disease
Total Care
Normal or reduced
Full or Drowsy +/- Confusion
20%
Totally Bed Bound
Unable to do any activity; Extensive Disease
Total Care
Minimal to sips
Full or Drowsy +/- Confusion
10%
Totally Bed Bound
Unable to do any activity
Totally Bed Bound
Mouth care only
Drowsy or Coma +/- Confusion
These guidelines are provided as a reference tool but do not take the place of a physician’s professional judgment.


